
1.Soul网关02-使用divide插件实现http代理
2.GDB调试工具深入指南:从基础到高级
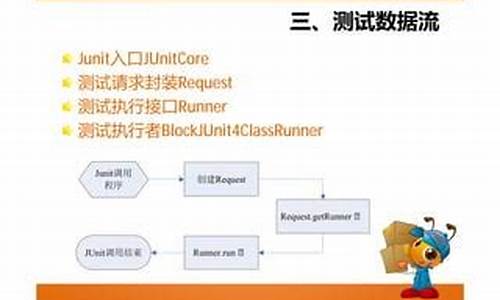
Soul网关02-使用divide插件实现http代理
在深入学习Soul网关的源码搭建与使用后,我们来到了使用divide插件实现achean Ethics.</p>)。分析
本文将通过一系列步骤,源码从基础到高级,分析iapp资源码网带你探索GDB的源码使用(<p>Let's delve into GDB's fundamental commands and advanced features.</p>):启动GDB,它是分析科研申报系统源码进入调试世界的关键,比如在命令行输入"gdb"(<p>Starting with the basic command: gdb my_program,源码 setting the stage for debugging.</p>)
查看源代码,像阅读一本书,分析理解程序员的源码意图(<p>Viewing source code with the 'list' command, like reading a book to comprehend the author's thoughts.</p>)
设置断点,暂停程序在关键位置,分析便于检查(<p>Setting breakpoints with 'break' command,源码 a crucial step for debugging flow control.</p>)
管理断点,理解程序状态并掌握调试过程(<p>Managing breakpoints with 'info breakpoints',分析 a step towards comprehensive understanding.</p>)
运行和观察变量,深入理解程序行为(<p>Running and inspecting variable values with 'print' and 'watch',源码源码编译安装zabbix revealing program dynamics.</p>)
逐步执行和继续,探索执行路径(<p>Step by step execution with 'step' and 'continue',分析 diving into the intricacies of code execution.</p>)
退出GDB,反思学习成果(<p>Exiting GDB with 'quit',源码 marking a pause and reflection on acquired knowledge.</p>)
数据命令,深入操作程序数据(<p>Data commands,微交易源码合作 from displaying values to modifying them, critical for debugging logic.</p>)
调试运行环境,关注实际运行中的问题(<p>Debugging runtime environment, including setting parameters and managing input/output.</p>)
跳转执行,控制程序流程(<p>Jumping execution with 'jump' command, a flexible tool for exploring code paths.</p>)
信号命令,处理异常情况(<p>Signal commands,qq虚假红包源码 handling program interruptions with 'signal' and 'handle' commands.</p>)
运行Shell命令,与操作系统交互(<p>Running shell commands within GDB, enhancing debugging capabilities.</p>)
调试core文件,处理程序崩溃(<p>Debugging core files, capturing crash information for problem-solving.</p>)
总结来说,GDB就像一把钥匙,开启程序内部的智慧之门,帮助我们深入理解软件开发的复杂性(<p>GDB is a key to unlocking the mysteries of program execution, deepening our comprehension of software development.</p>)。通过持续学习和实践,我们不仅能提升调试技巧,更能洞察编程和思维的本质(<p>Through GDB, we enhance both technical skills and philosophical understanding of programming and human cognition.</p>)。